The Science
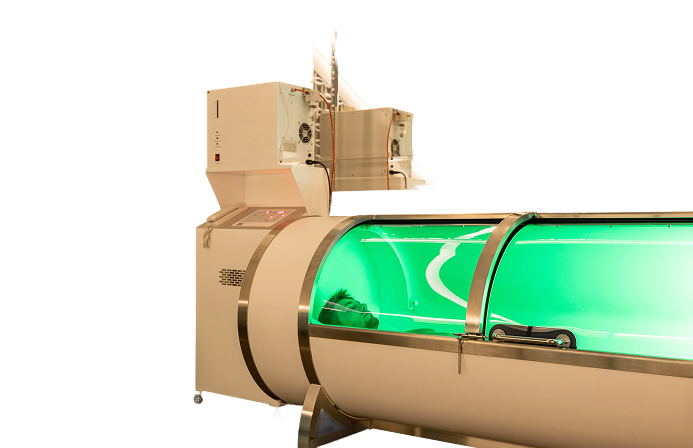
HBOT has been used in clinical settings since the 1960s and is supported by decades of research examining oxygen’s role in healing and recovery. It is well established in medical contexts such as wound healing, decompression sickness, radiation injury, and certain neurological conditions.
When oxygen is delivered under pressure, it enhances cellular metabolism, supports tissue repair processes, and improves oxygen diffusion into areas that may otherwise be oxygen-deprived. Research also suggests HBOT may stimulate stem cell mobilization and influence markers associated with cellular aging, including telomere dynamics, though this area continues to be actively studied.
By increasing oxygen delivery beyond what is possible with normal breathing, HBOT provides the body with a foundational resource required for repair, resilience, and functional optimization.